AMETROPIAS
(OR VISUAL DISORDERS)
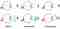
An emmetropic eye is defined as an eye that has no refractive defects and therefore exhibits a visual acuity of 10/10 in both distance and proximal vision.
Hypermetropia is a visual defect concerning the ability to see near objects well, in which light rays from distant objects, instead of arriving correctly on the retina of the eye, focus beyond it, thus making vision at all distances blurry. In hypermetropia, accommodation is always active, both for near and far, and this causes visual fatigue, blurring of images especially for near, tearing, and headaches. These disorders are categorised as asthenopia.
It is a vision defect that results in reduced visual clarity due to a deformation of the surface of the eye (i.e. the cornea) or an alteration of the internal structures of the eyeball. The cornea of the eye with astigmatism is similar to a small rugby ball: the curvature is not the same over the entire surface and, therefore, the light rays are not all focused on the retina. This causes, in milder cases, less sharpness or splitting of images and in more severe cases, distortion of objects: a circle, for example, is perceived as an oval shape. Astigmatism worsens both distance and near vision and has no relation to the person's age; it can be present from birth and can be associated with myopia, hypermetropia and presbyopia, sometimes even with different combinations of the different visual deficits. The main consequence of astigmatism is an unclear vision of images and therefore needs to be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Visual deficit due to the loss of accommodation and focusing capacity by the crystalline lens, resulting in blurred vision at near distance, i.e. reading and all near activities 40-50 cm. Compensation of presbyopia: it is first of all necessary to point out that the use or non-use of optical prescription does not in any way affect the evolution of presbyopia, which will in any case be progressive, until the total loss of accommodation around the age of 60.
Visual impairment that does not allow good distance vision, creating considerable difficulties in driving, watching TV, recognising objects and people at a distance.








